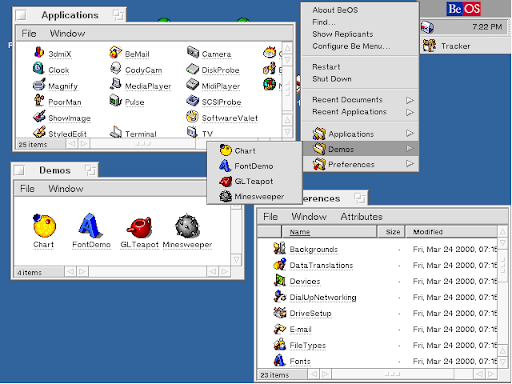
In the ever-evolving world of technology, certain stories capture our imagination more than others, especially when they involve innovations that promised to change the course of history. One such captivating tale is that of BeOS, an operating system that once seemed poised to revolutionize personal computing. Born in the mid-1990s, an era teeming with technological innovation and the dawn of the internet age, BeOS emerged as a bright star in a sky crowded with early contenders. With its impressive capabilities, sleek design, and forward-thinking architecture, BeOS captured the attention of tech enthusiasts and industry insiders alike, sparking a wave of excitement and speculation about its potential to challenge the status quo. But why, then, did this revolutionary system fade into obscurity? 🌟
To truly understand the rise and fall of BeOS, we must first delve into its origins, a story marked by ambition, creativity, and a quest for perfection. Developed by Be Inc., a company founded by Jean-Louis Gassée, a former Apple executive, BeOS was crafted with a singular vision: to create an operating system that was not only powerful and efficient but also intuitive and accessible. Unlike its contemporaries, BeOS was designed from the ground up to take advantage of modern hardware, offering features like symmetric multiprocessing, a journaling file system, and real-time capabilities that were groundbreaking at the time. Its clean, modern interface and remarkable speed set it apart, positioning it as a potential game-changer in the world of operating systems.
However, as we explore the rise of BeOS, it becomes evident that the journey was fraught with challenges and pivotal decisions that would ultimately seal its fate. Despite its technical brilliance, BeOS struggled to find its footing in a market dominated by giants like Microsoft and Apple. The story of BeOS is not just one of technological achievement but also one of strategic missteps, market dynamics, and the harsh realities of the competitive tech landscape. From its initial development to its ill-fated negotiations with Apple and eventual acquisition by Palm, the path of BeOS is a tapestry of ambition, innovation, and unforeseen obstacles that provides a rich case study in both the triumphs and pitfalls of technological advancement.
In this article, we will uncover the mystery of BeOS by examining its inception, the groundbreaking features that set it apart, and the series of events that led to its decline. Through interviews with former employees, insights from industry experts, and a comprehensive analysis of historical documents, we aim to piece together the intricate puzzle of BeOS’s rise and fall. Join us on this journey as we explore how an operating system that once held so much promise faded into the annals of tech history, offering valuable lessons for innovators and entrepreneurs in today’s fast-paced digital world. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a history buff, or simply curious about the forces that shape our digital landscape, this deep dive into the story of BeOS promises to be both enlightening and thought-provoking. 🔍
Introduction to BeOS: A Revolutionary Operating System
BeOS was developed by Be Inc. in the mid-1990s as a new operating system designed to take advantage of the latest hardware advancements, particularly in the realm of multimedia processing. It was a time when the computing world was predominantly dominated by Microsoft Windows and Apple’s Mac OS, and BeOS aimed to provide a fresh alternative with unique capabilities and a sleek interface.
The origins of BeOS trace back to Jean-Louis Gassée, a former Apple executive, who founded Be Inc. in 1990. The vision was clear: create an operating system that was both powerful and easy to use, targeting the multimedia market that was rapidly expanding with the rise of digital media. BeOS was designed to leverage symmetric multiprocessing, pervasive multithreading, and a 64-bit journaling file system, making it a strong contender in handling the intensive demands of audio and video processing.
Despite its innovative features, BeOS struggled to gain a foothold in the market. As we delve deeper into the rise and fall of BeOS, it becomes evident that a combination of strategic missteps, market conditions, and fierce competition played crucial roles in its eventual obscurity. Yet, the legacy of BeOS lives on, influencing modern operating systems and continuing to capture the imagination of tech enthusiasts.
The Technical Marvel of BeOS
One of the standout features of BeOS was its ability to efficiently handle multimedia tasks, thanks to its modular architecture. The operating system was designed to support preemptive multitasking and symmetric multiprocessing from the ground up, which allowed it to effectively utilize multiple CPU cores. This was a significant advantage at a time when most consumer operating systems struggled with these concepts.
Moreover, BeOS introduced the BFS (Be File System), which was a 64-bit journaling file system known for its speed and robustness. BFS supported large file sizes and metadata indexing, making it particularly suited for multimedia files. This was complemented by a highly responsive GUI (Graphical User Interface) that was both user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing, drawing favorable comparisons to other operating systems of the time.
Another innovative aspect of BeOS was its pervasive multithreading, which allowed applications to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. This was particularly beneficial for multimedia applications, as it enabled smooth playback and editing of audio and video files without taxing the system resources excessively. The real-time capabilities of BeOS also made it an attractive option for creative professionals who required precision and reliability in their software tools.
Market Struggles and Strategic Missteps
Despite its technical prowess, BeOS faced significant challenges in gaining market traction. One of the primary hurdles was the dominance of Microsoft Windows and the limited market share of alternative operating systems. BeOS was unable to secure partnerships with major hardware manufacturers, which limited its distribution and accessibility to a wider audience.
A significant setback came when Be Inc. attempted to sell BeOS to Apple as a replacement for Mac OS. Although the negotiations seemed promising, Apple ultimately chose to acquire NeXT, founded by Steve Jobs, which led to the development of Mac OS X. This decision left BeOS without a major platform to support its growth and expansion.
Furthermore, Be Inc.’s focus on the niche multimedia market may have restricted its appeal to a broader consumer base. While BeOS was well-regarded for its capabilities, the general computing public was already entrenched in the ecosystems provided by Windows and Mac OS. The lack of widespread software support and compatibility further hindered its adoption.
Comparative Analysis: BeOS vs. Contemporary Operating Systems
To understand the position of BeOS in the computing landscape, it’s essential to compare it with the operating systems available during its time. Below is a comparative table highlighting key aspects of BeOS, Windows 95/98, and Mac OS 8/9.
| Feature | BeOS | Windows 95/98 | Mac OS 8/9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multitasking | Preemptive | Cooperative/Preemptive | Cooperative |
| Multiprocessing | Symmetric | Limited support | Limited support |
| File System | BFS (64-bit journaling) | FAT32 | HFS+ |
| User Interface | Responsive and modular | Classic Windows GUI | Classic Mac OS GUI |
| Target Market | Multimedia professionals | General consumers | Creative professionals |
The table above illustrates the strengths of BeOS, particularly in terms of multitasking and multiprocessing capabilities. However, its market niche and lack of widespread hardware support limited its competitiveness against more established systems. For a deeper dive into the technical marvel that was BeOS, you can watch this insightful video: The Rise and Fall of BeOS – Techquickie.
The Legacy of BeOS
Although BeOS ultimately faded into obscurity, its legacy persists in various ways. The operating system’s architecture and innovative features have inspired subsequent developments in software design, influencing the evolution of modern operating systems. Concepts such as preemptive multitasking, symmetric multiprocessing, and advanced file systems have become standard in today’s computing environments, thanks in part to the pioneering efforts of BeOS.
Additionally, the open-source community has kept the spirit of BeOS alive through projects like Haiku, an open-source operating system that aims to recreate and extend the BeOS experience. Haiku has attracted a dedicated community of developers and enthusiasts who continue to explore the possibilities of this unique platform.
- BeOS was a trailblazer in multimedia processing and user interface design.
- Strategic missteps and market conditions limited its widespread adoption.
- The legacy of BeOS lives on through open-source projects and its influence on modern operating systems.
As we reflect on the rise and fall of BeOS, it serves as a testament to the challenges of breaking into an established market and the importance of strategic vision in the tech industry. BeOS remains a fascinating chapter in the history of computing, offering valuable lessons and inspiration for future innovations.

Conclusion
In unraveling the enigma of BeOS, this article has traversed through the fascinating journey of an operating system that once promised to redefine the digital landscape. BeOS, with its avant-garde approach to multimedia handling, its highly efficient architecture, and its aesthetic interface, was a beacon of innovation in the mid-1990s. This conclusion encapsulates the essence of BeOS’s rise and fall, reflecting on its impact and the lessons it offers for future technological advancements.
We began by examining the birth of BeOS, a product of visionary minds at Be Inc., led by Jean-Louis Gassée. The operating system was crafted with a focus on multimedia processing, boasting a microkernel design that allowed for unmatched performance on the hardware of its time. BeOS was particularly celebrated for its preemptive multitasking, symmetric multiprocessing, and its 64-bit journaling file system, BFS, which collectively contributed to its robustness and agility. These features were designed to support the burgeoning needs of multimedia creators and consumers, making BeOS a darling among tech enthusiasts and developers alike.
Despite its technical prowess, BeOS’s journey was marred by strategic missteps and unfortunate circumstances. We explored how its inability to secure a dominant position in the market was exacerbated by stiff competition from established giants like Microsoft and Apple. The pivotal moment came when Apple, initially considering BeOS for its new line of computers, opted for NeXTSTEP instead, sealing BeOS’s fate in a market driven by aggressive corporate maneuvers and strategic partnerships.
Further analysis shed light on the challenges BeOS faced in terms of software compatibility and market penetration. With a limited application ecosystem, developers were hesitant to adopt BeOS, despite its superior technology. The lack of major software titles, coupled with a limited hardware base, restricted BeOS’s appeal to a niche audience. These factors, combined with a rapidly evolving technology landscape, led to BeOS’s gradual decline.
The narrative of BeOS is not just a tale of missed opportunities; it is also a testament to the importance of timing and market strategy in the technology industry. BeOS demonstrated that even the most advanced technologies can falter without the right support and positioning. This serves as a crucial lesson for innovators today: the need to balance technological excellence with strategic foresight.
As we reflect on the legacy of BeOS, it is essential to acknowledge its enduring influence on modern operating systems. Many of the features that were pioneering in BeOS have become standard in today’s OS architectures, such as efficient multitasking and robust file systems. BeOS’s emphasis on user experience and performance paved the way for future developments, influencing the design philosophies of contemporary systems.
In closing, the story of BeOS is both a cautionary tale and an inspiring saga of innovation. It reminds us of the transient nature of technological supremacy and the relentless pace of progress. However, it also serves as a beacon for the relentless pursuit of innovation, encouraging us to push the boundaries of what is possible in technology.
As we bid farewell to the tale of BeOS, let us carry forward its spirit of innovation and excellence. We encourage you, dear reader, to reflect on the lessons from BeOS’s journey. Consider how these insights can be applied to current and future technological endeavors. Share your thoughts and insights, engage with others in the tech community, and continue the conversation about how we can learn from the past to shape a more innovative future. 🌟
If you want to dive deeper into the world of BeOS, its development, and its legacy, here are some resources you might find interesting:
– Haiku OS – A project that continues the spirit of BeOS.
– BeOS Retrospective – An article exploring the broader implications of BeOS’s strategies.
– BeOS Documentation – A treasure trove of original documentation and user guides.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of BeOS. We hope it has inspired you to appreciate the intricacies of operating system design and the factors that influence technological success and failure. Feel free to share this article with others who might find it enlightening, and let us know your thoughts in the comments. Let’s keep the spirit of innovation alive! 🚀
Toni Santos is a visual historian and creative artisan whose work channels the bold spirit of the steam-powered era—a time when imagination, mechanics, and ambition converged to reshape the modern world. Through richly detailed visual narratives and handcrafted design, Toni celebrates the legacy of steam innovation as both an artistic and technological revolution.
Driven by a passion for mechanical aesthetics, forgotten inventions, and industrial-age ingenuity, Toni reimagines the world of steam through illustrations, tactile artifacts, and storytelling that capture the poetry of pressure, motion, and invention. From piston-driven engines to brass-detailed diagrams, each piece reveals how steam wasn’t just power—it was promise.
With a background in visual design and historical research, Toni brings a craftsman’s eye and a dreamer’s heart to the stories of tinkerers, inventors, and visionaries who shaped the 19th century. His work doesn’t merely document machines—it honors the culture, courage, and creativity that drove a world to reimagine itself through gears, valves, and vapor.
As the creative voice behind Vizovex, Toni shares curated articles, reconstructed blueprints, and visual interpretations that bring this industrial past to life. His collections serve as a tribute to:
The elegance of steam-era design and innovation
The human stories behind great mechanical feats
The aesthetic beauty found in function and form
The echo of invention in today’s creative world
Whether you’re a history lover, a fan of steampunk, or an admirer of antique technology, Toni welcomes you into a world where art and machinery fuse, one cog, one drawing, one rediscovered marvel at a time.